|  |  |  |
Current transformers are designed to convert high primary current levels into secondary currents of a lower, more manageable magnitude, typically 5 Amperes or 1 Ampere. This facilitates the seamless integration of the current into measuring instruments and other critical devices, such as relays, which monitor the primary current. In instances where the connecting leads are exceptionally long, it is advisable to opt for a secondary current of 1 Ampere rather than 5 Amperes. This strategic choice is made to reduce the voltage-ampere (VA) load on the current transformer, thereby enhancing its operational efficiency and accuracy in current measurement.
Types of Current Transformers
- Metering Current Transformers: Current Transformers (CTs) are integral components in power measurement systems, providing critical data to devices such as ammeters and watt meters. They are engineered for precision, with accuracy classifications ranging from 5% to 120% of nominal current ratings. To ensure the protection of these instruments, CTs are designed to reach saturation between 150% and 200% of their rated current, thereby safeguarding against potentially damaging current spikes during system anomalies.
- Core Balance Current Transformers: used in conjunction with Earth Fault Relays to detect earth fault currents.
In terms of structure, Current Transformers (CTs) are classified into two types:
- Bar Primary CTs: This category exclusively comprises of secondary windings. The CT is mounted onto a bus bar, which serves as a single-turn primary conductor. However, Bar Primary CTs are generally not recommended for applications with rated currents under 100 Amps. This is due to the inadequate ampere-turns, which are essential to compensate for losses and burdens efficiently while delivering accuracies of 1% or better.
- Wound Primary CTs: These transformers are equipped with both primary and secondary windings. The primary winding is configured with enough turns to achieve the necessary ampere-turns, facilitating the attainment of accuracies of 1% or finer.
Each type is engineered to fulfill specific electrical criteria and accuracy standards, ensuring suitability for diverse applications and electrical infrastructure.
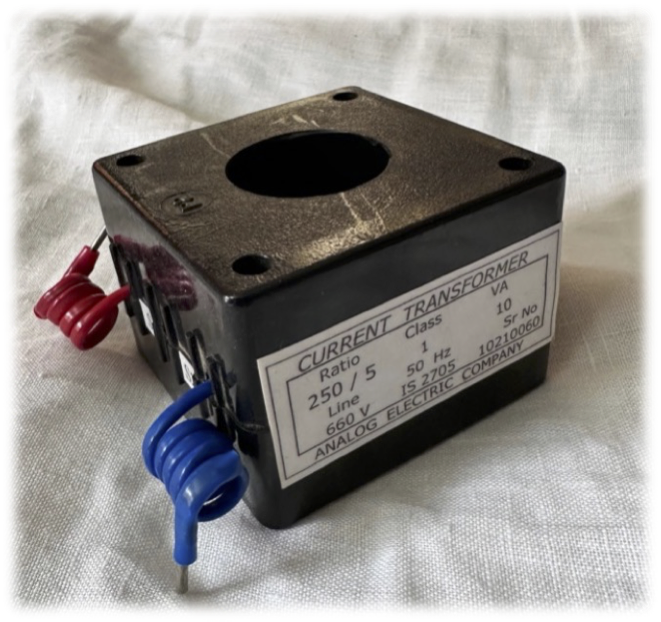
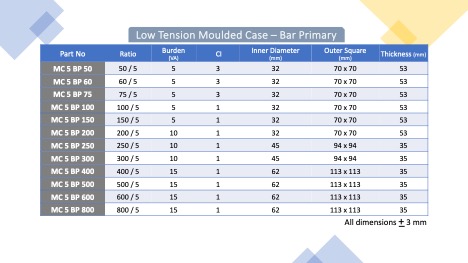
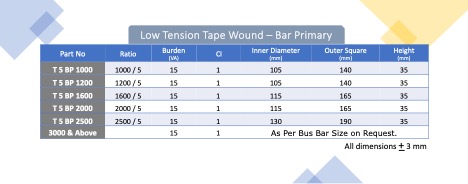
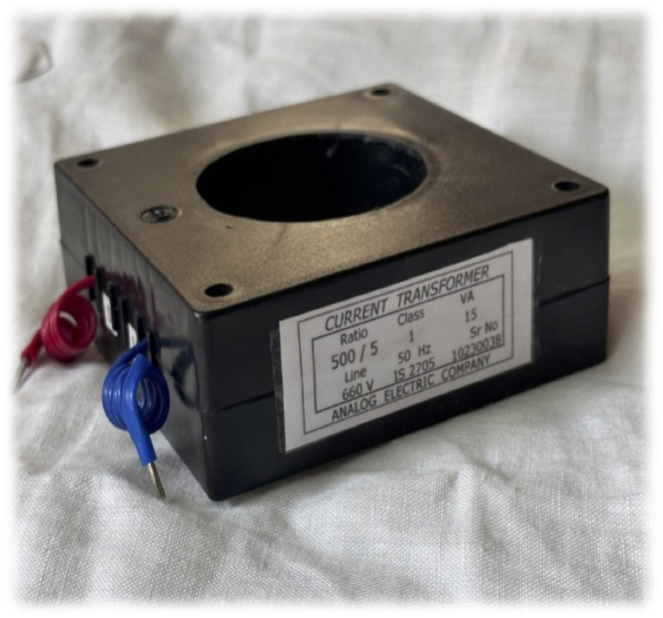
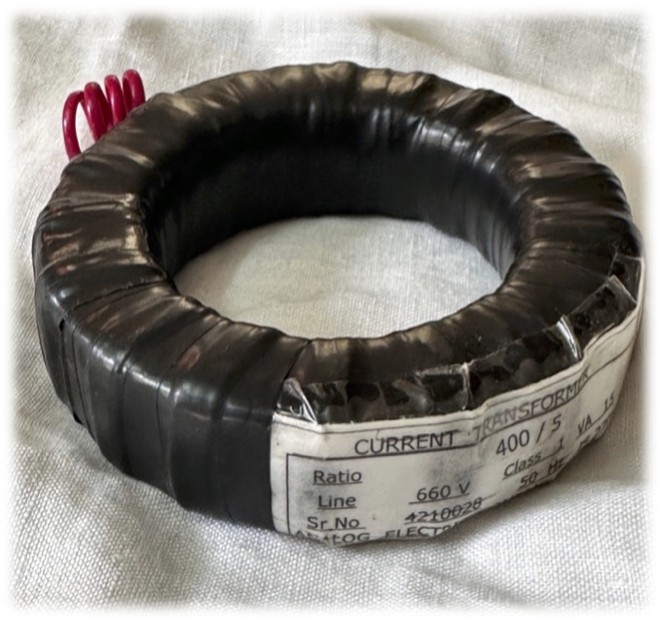
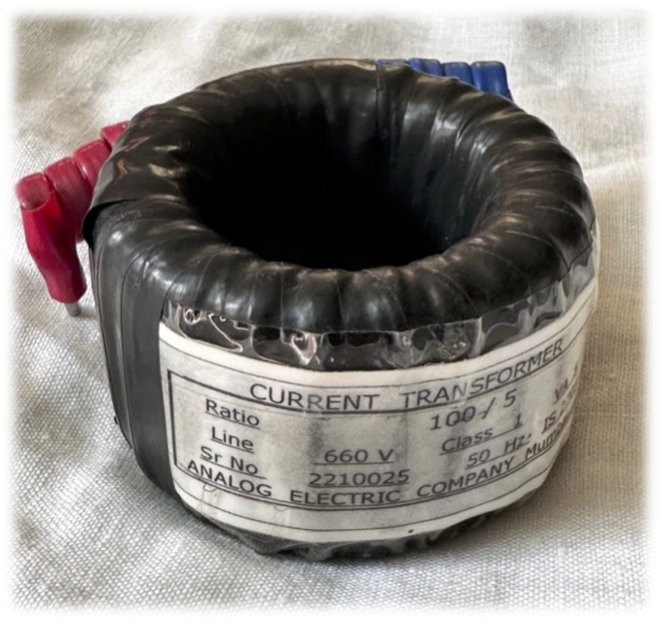
Our CTs come two different enclosures viz. “PVC Wound Tape” and “ABS Mould Case”.
Our Current Transformers (CTs) are constructed using premium-grade Cold-Rolled Grain-Oriented (CRGO) silicon steel, meticulously formed into a toroidal shape without joints to ensure optimal accuracy. The coils are crafted from high-quality electrical-grade copper, with interlayer insulation provided by polyester tape. The final insulation is achieved through one of three methods: ABS molding, resin casting, or PVC taping, depending on application requirements. Rigorous quality control measures are implemented at every stage of production for each CT. Comprehensive routine testing is performed, with the results meticulously documented. Detailed test reports for individual CTs can be furnished upon request to guarantee transparency and quality assurance.
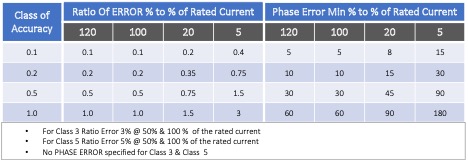
Limit of Error per accuracy class
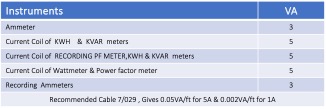
Typical VA Burdens of Different Meters
![]()
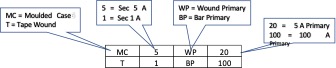
Explanation of Part Number